A source is one of the folders you need to synchronize.
Actually it may any valid local folder (like "c:\") or UNC
folder (like "\\server1\shared\").
You can add one or by clicking from menu or
from the toolbar, or by dropping folders directly from Explorer.
If you drag a file, the program gets its folder as a source. If a folder is
already included into a source, it's ignored.
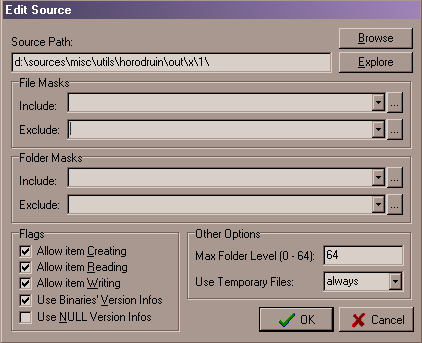
When you insert a new folder or edit an existing one the following dialog will pop up.

When you press OK button, the program tries to verify the given folder. It must not be included into another source.
| Source Path | The folder you need to synchronize. Actually you can only use local or (UNC) remote folders. To fill it, you can type the value in it, or simply by using the Browse button. Sometimes it's possible that, you can't locate a network folder by browsing it. Try to explore it, and when you have found it, you can paste the proper path into its dialog field. |
||||||
| Explore | If you wish to peek into the folder, just click the Explore button and and explorer window will pop up (only if the folder exist). | ||||||
| File/Folder Masks |
|
||||||
| Flags |
|
||||||
| Max Folder Level | This is the maximum folder level you need to recurse. | ||||||
| Use temp. Files | This rules on temporary file usage during the
synchronization process.
Actually you have 3 options:
|
||||||
| Use Bin. Ver. Infos | This enable/disable the file version handling. Using
it will improve binaries file comparison but it affect the analysis speed. Remember, a file without version infos is considered always older than a file with these infos. So, if you are in need to disable it in one source, it's better to do it in all other sources too. |
Note: whenever you change source's options, you will loose all its collected data and you will have to analyze sources' contents again.
After having setup all the needed sources, there are things we can do with them.
The first one is the order them from the quickest (usually local folders)
from the slowest.
Although the program should catalog the source type, the order may have some
effect on choosing file newest candidate (if there are many copies of it).
The source order is recorded into the program data files.
If a source doesn't need to be updated very frequently (a slow device, a
removable disk, a mobile PC), it can be disabled.
Disabled sources are simply ignored (no analysis, no synchronization).
This status is recorded into the program data files.
If we need to synchronize the source, we have to analyze them.
After this task, the source is filled with source's contents stats data.
Once filled a source will not be analyzed again. To force it, we can
invalidate source data.
This allows to do something like to load and analyze all the enabled sources,
enabling a disabled one and analyze it too (without processing the filled ones
anymore).
Finally if we need to see and alter the source result, we can always use the Source Result Viewer window.